 View on TensorFlow.org
View on TensorFlow.org
|
 Run in Google Colab
Run in Google Colab
|
 View source on GitHub
View source on GitHub
|
 Download notebook Download notebook
|
This tutorial introduces autoencoders with three examples: the basics, image denoising, and anomaly detection.
An autoencoder is a special type of neural network that is trained to copy its input to its output. For example, given an image of a handwritten digit, an autoencoder first encodes the image into a lower dimensional latent representation, then decodes the latent representation back to an image. An autoencoder learns to compress the data while minimizing the reconstruction error.
To learn more about autoencoders, please consider reading chapter 14 from Deep Learning by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville.
Import TensorFlow and other libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from tensorflow.keras import layers, losses
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import fashion_mnist
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
2024-07-19 01:34:38.577118: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:485] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered 2024-07-19 01:34:38.597940: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:8454] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered 2024-07-19 01:34:38.604259: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1452] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
Load the dataset
To start, you will train the basic autoencoder using the Fashion MNIST dataset. Each image in this dataset is 28x28 pixels.
(x_train, _), (x_test, _) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
print (x_train.shape)
print (x_test.shape)
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz 29515/29515 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz 26421880/26421880 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz 5148/5148 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz 4422102/4422102 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step (60000, 28, 28) (10000, 28, 28)
First example: Basic autoencoder
Define an autoencoder with two Dense layers: an encoder, which compresses the images into a 64 dimensional latent vector, and a decoder, that reconstructs the original image from the latent space.
To define your model, use the Keras Model Subclassing API.
class Autoencoder(Model):
def __init__(self, latent_dim, shape):
super(Autoencoder, self).__init__()
self.latent_dim = latent_dim
self.shape = shape
self.encoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(latent_dim, activation='relu'),
])
self.decoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(tf.math.reduce_prod(shape).numpy(), activation='sigmoid'),
layers.Reshape(shape)
])
def call(self, x):
encoded = self.encoder(x)
decoded = self.decoder(encoded)
return decoded
shape = x_test.shape[1:]
latent_dim = 64
autoencoder = Autoencoder(latent_dim, shape)
WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR I0000 00:00:1721352882.295547 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.299415 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.302977 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.306555 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.317911 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.321456 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.324803 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.328236 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.331593 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.334951 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.338368 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352882.341848 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.589512 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.591771 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.593770 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.595852 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.598075 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.600171 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.602045 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.604032 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.606144 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.608215 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.610099 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.612100 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.650350 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.652536 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.654463 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.656496 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.658633 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.660717 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.662587 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.664545 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.666746 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.669465 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.671789 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355 I0000 00:00:1721352883.674211 23008 cuda_executor.cc:1015] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero. See more at https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.0/Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-pci#L344-L355
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=losses.MeanSquaredError())
Train the model using x_train as both the input and the target. The encoder will learn to compress the dataset from 784 dimensions to the latent space, and the decoder will learn to reconstruct the original images.
.
autoencoder.fit(x_train, x_train,
epochs=10,
shuffle=True,
validation_data=(x_test, x_test))
Epoch 1/10 WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR I0000 00:00:1721352885.729397 23175 service.cc:146] XLA service 0x7fbe4c008de0 initialized for platform CUDA (this does not guarantee that XLA will be used). Devices: I0000 00:00:1721352885.729441 23175 service.cc:154] StreamExecutor device (0): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5 I0000 00:00:1721352885.729445 23175 service.cc:154] StreamExecutor device (1): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5 I0000 00:00:1721352885.729448 23175 service.cc:154] StreamExecutor device (2): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5 I0000 00:00:1721352885.729451 23175 service.cc:154] StreamExecutor device (3): Tesla T4, Compute Capability 7.5 142/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 1ms/step - loss: 0.1013 I0000 00:00:1721352886.371904 23175 device_compiler.h:188] Compiled cluster using XLA! This line is logged at most once for the lifetime of the process. 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 4s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0403 - val_loss: 0.0132 Epoch 2/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0123 - val_loss: 0.0106 Epoch 3/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0102 - val_loss: 0.0097 Epoch 4/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0095 - val_loss: 0.0093 Epoch 5/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0092 - val_loss: 0.0093 Epoch 6/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0090 - val_loss: 0.0090 Epoch 7/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0088 - val_loss: 0.0090 Epoch 8/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0088 - val_loss: 0.0089 Epoch 9/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0088 - val_loss: 0.0088 Epoch 10/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0087 - val_loss: 0.0088 <keras.src.callbacks.history.History at 0x7fc008462fa0>
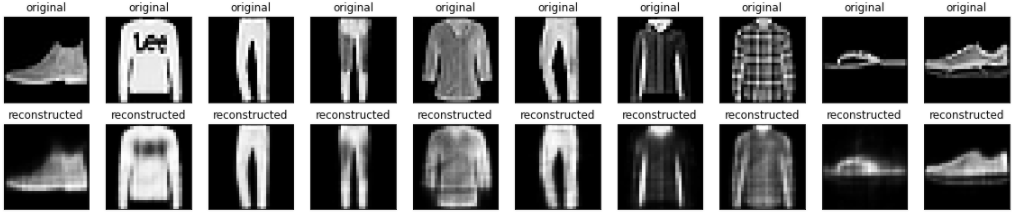
Now that the model is trained, let's test it by encoding and decoding images from the test set.
encoded_imgs = autoencoder.encoder(x_test).numpy()
decoded_imgs = autoencoder.decoder(encoded_imgs).numpy()
n = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(n):
# display original
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1)
plt.imshow(x_test[i])
plt.title("original")
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
# display reconstruction
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1 + n)
plt.imshow(decoded_imgs[i])
plt.title("reconstructed")
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()

Second example: Image denoising
An autoencoder can also be trained to remove noise from images. In the following section, you will create a noisy version of the Fashion MNIST dataset by applying random noise to each image. You will then train an autoencoder using the noisy image as input, and the original image as the target.
Let's reimport the dataset to omit the modifications made earlier.
(x_train, _), (x_test, _) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
x_train = x_train[..., tf.newaxis]
x_test = x_test[..., tf.newaxis]
print(x_train.shape)
(60000, 28, 28, 1)
Adding random noise to the images
noise_factor = 0.2
x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_factor * tf.random.normal(shape=x_train.shape)
x_test_noisy = x_test + noise_factor * tf.random.normal(shape=x_test.shape)
x_train_noisy = tf.clip_by_value(x_train_noisy, clip_value_min=0., clip_value_max=1.)
x_test_noisy = tf.clip_by_value(x_test_noisy, clip_value_min=0., clip_value_max=1.)
Plot the noisy images.
n = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 2))
for i in range(n):
ax = plt.subplot(1, n, i + 1)
plt.title("original + noise")
plt.imshow(tf.squeeze(x_test_noisy[i]))
plt.gray()
plt.show()
Define a convolutional autoencoder
In this example, you will train a convolutional autoencoder using Conv2D layers in the encoder, and Conv2DTranspose layers in the decoder.
class Denoise(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(Denoise, self).__init__()
self.encoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Input(shape=(28, 28, 1)),
layers.Conv2D(16, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', strides=2),
layers.Conv2D(8, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', strides=2)])
self.decoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Conv2DTranspose(8, kernel_size=3, strides=2, activation='relu', padding='same'),
layers.Conv2DTranspose(16, kernel_size=3, strides=2, activation='relu', padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(1, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='sigmoid', padding='same')])
def call(self, x):
encoded = self.encoder(x)
decoded = self.decoder(encoded)
return decoded
autoencoder = Denoise()
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=losses.MeanSquaredError())
autoencoder.fit(x_train_noisy, x_train,
epochs=10,
shuffle=True,
validation_data=(x_test_noisy, x_test))
Epoch 1/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 7s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0383 - val_loss: 0.0111 Epoch 2/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0107 - val_loss: 0.0099 Epoch 3/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 4s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0097 - val_loss: 0.0094 Epoch 4/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 4s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0093 - val_loss: 0.0091 Epoch 5/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 4s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0089 - val_loss: 0.0087 Epoch 6/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 4s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0084 - val_loss: 0.0082 Epoch 7/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0081 - val_loss: 0.0080 Epoch 8/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 4s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0079 - val_loss: 0.0078 Epoch 9/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 4s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0079 - val_loss: 0.0078 Epoch 10/10 1875/1875 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 4s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0078 - val_loss: 0.0077 <keras.src.callbacks.history.History at 0x7fc017ac5c70>
Let's take a look at a summary of the encoder. Notice how the images are downsampled from 28x28 to 7x7.
autoencoder.encoder.summary()
The decoder upsamples the images back from 7x7 to 28x28.
autoencoder.decoder.summary()
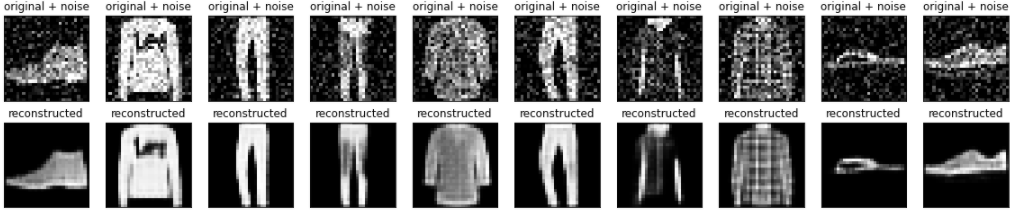
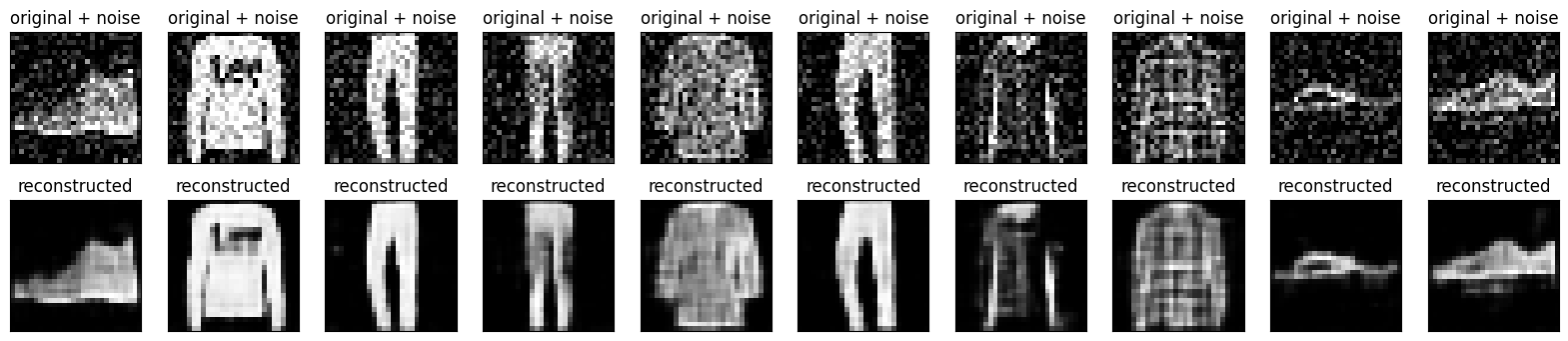
Plotting both the noisy images and the denoised images produced by the autoencoder.
encoded_imgs = autoencoder.encoder(x_test_noisy).numpy()
decoded_imgs = autoencoder.decoder(encoded_imgs).numpy()
W0000 00:00:1721352953.958381 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352953.977001 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352953.979016 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352953.981126 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352953.983229 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352953.986197 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352953.988619 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352953.991553 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352953.994704 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352953.997259 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.001698 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.004610 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.009705 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.014051 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.023790 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.038732 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.041209 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.043856 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.047107 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.050614 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.054351 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.060253 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.065635 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.070927 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.078616 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.085602 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.088252 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.090680 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.093489 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.096751 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.100334 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.137697 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.141986 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.145588 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.149917 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.161306 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.165332 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.173184 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.179994 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.200042 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.216489 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.245249 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.265195 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.290166 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.314617 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.331780 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.353586 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.402914 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.424736 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.554577 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.564572 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.583514 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.605556 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.639923 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.654178 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.688278 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.754403 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.804660 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.893250 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.911267 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.928996 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.951555 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.988040 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352954.998764 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352955.036812 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced W0000 00:00:1721352955.062787 23008 gpu_timer.cc:114] Skipping the delay kernel, measurement accuracy will be reduced
n = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(n):
# display original + noise
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1)
plt.title("original + noise")
plt.imshow(tf.squeeze(x_test_noisy[i]))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
# display reconstruction
bx = plt.subplot(2, n, i + n + 1)
plt.title("reconstructed")
plt.imshow(tf.squeeze(decoded_imgs[i]))
plt.gray()
bx.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
bx.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
Third example: Anomaly detection
Overview
In this example, you will train an autoencoder to detect anomalies on the ECG5000 dataset. This dataset contains 5,000 Electrocardiograms, each with 140 data points. You will use a simplified version of the dataset, where each example has been labeled either 0 (corresponding to an abnormal rhythm), or 1 (corresponding to a normal rhythm). You are interested in identifying the abnormal rhythms.
How will you detect anomalies using an autoencoder? Recall that an autoencoder is trained to minimize reconstruction error. You will train an autoencoder on the normal rhythms only, then use it to reconstruct all the data. Our hypothesis is that the abnormal rhythms will have higher reconstruction error. You will then classify a rhythm as an anomaly if the reconstruction error surpasses a fixed threshold.
Load ECG data
The dataset you will use is based on one from timeseriesclassification.com.
# Download the dataset
dataframe = pd.read_csv('http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/ecg.csv', header=None)
raw_data = dataframe.values
dataframe.head()
# The last element contains the labels
labels = raw_data[:, -1]
# The other data points are the electrocadriogram data
data = raw_data[:, 0:-1]
train_data, test_data, train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(
data, labels, test_size=0.2, random_state=21
)
Normalize the data to [0,1].
min_val = tf.reduce_min(train_data)
max_val = tf.reduce_max(train_data)
train_data = (train_data - min_val) / (max_val - min_val)
test_data = (test_data - min_val) / (max_val - min_val)
train_data = tf.cast(train_data, tf.float32)
test_data = tf.cast(test_data, tf.float32)
You will train the autoencoder using only the normal rhythms, which are labeled in this dataset as 1. Separate the normal rhythms from the abnormal rhythms.
train_labels = train_labels.astype(bool)
test_labels = test_labels.astype(bool)
normal_train_data = train_data[train_labels]
normal_test_data = test_data[test_labels]
anomalous_train_data = train_data[~train_labels]
anomalous_test_data = test_data[~test_labels]
Plot a normal ECG.
plt.grid()
plt.plot(np.arange(140), normal_train_data[0])
plt.title("A Normal ECG")
plt.show()
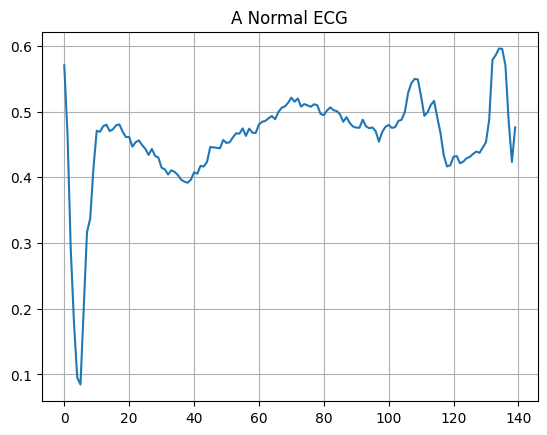
Plot an anomalous ECG.
plt.grid()
plt.plot(np.arange(140), anomalous_train_data[0])
plt.title("An Anomalous ECG")
plt.show()
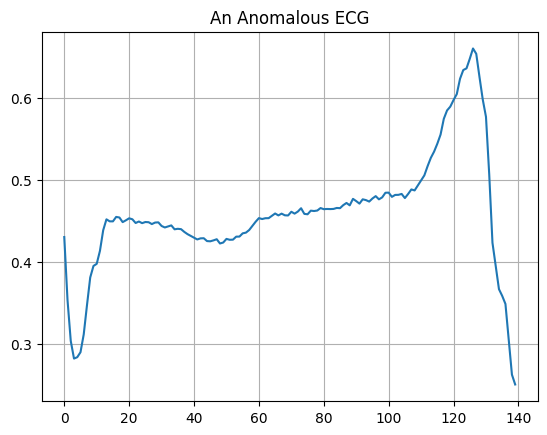
Build the model
class AnomalyDetector(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(AnomalyDetector, self).__init__()
self.encoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(32, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(16, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(8, activation="relu")])
self.decoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(16, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(32, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(140, activation="sigmoid")])
def call(self, x):
encoded = self.encoder(x)
decoded = self.decoder(encoded)
return decoded
autoencoder = AnomalyDetector()
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mae')
Notice that the autoencoder is trained using only the normal ECGs, but is evaluated using the full test set.
history = autoencoder.fit(normal_train_data, normal_train_data,
epochs=20,
batch_size=512,
validation_data=(test_data, test_data),
shuffle=True)
Epoch 1/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 503ms/step - loss: 0.0604 - val_loss: 0.0539 Epoch 2/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0573 - val_loss: 0.0528 Epoch 3/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0559 - val_loss: 0.0516 Epoch 4/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0544 - val_loss: 0.0503 Epoch 5/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0522 - val_loss: 0.0486 Epoch 6/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0488 - val_loss: 0.0470 Epoch 7/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0446 - val_loss: 0.0454 Epoch 8/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0407 - val_loss: 0.0433 Epoch 9/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0373 - val_loss: 0.0417 Epoch 10/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0344 - val_loss: 0.0410 Epoch 11/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 12ms/step - loss: 0.0321 - val_loss: 0.0397 Epoch 12/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 12ms/step - loss: 0.0302 - val_loss: 0.0389 Epoch 13/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0287 - val_loss: 0.0381 Epoch 14/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 12ms/step - loss: 0.0275 - val_loss: 0.0372 Epoch 15/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 12ms/step - loss: 0.0264 - val_loss: 0.0366 Epoch 16/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0256 - val_loss: 0.0358 Epoch 17/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0249 - val_loss: 0.0353 Epoch 18/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0243 - val_loss: 0.0348 Epoch 19/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0236 - val_loss: 0.0344 Epoch 20/20 5/5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.0228 - val_loss: 0.0340
plt.plot(history.history["loss"], label="Training Loss")
plt.plot(history.history["val_loss"], label="Validation Loss")
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fc016981f10>
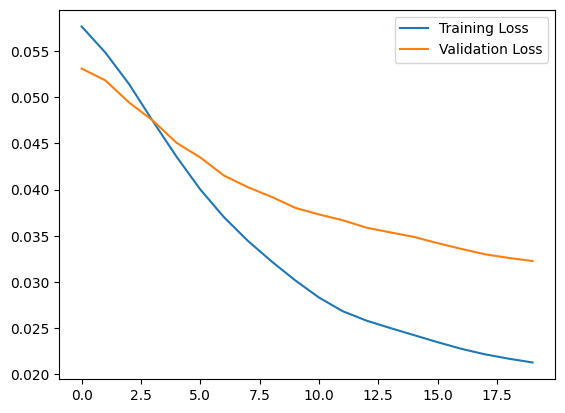
You will soon classify an ECG as anomalous if the reconstruction error is greater than one standard deviation from the normal training examples. First, let's plot a normal ECG from the training set, the reconstruction after it's encoded and decoded by the autoencoder, and the reconstruction error.
encoded_data = autoencoder.encoder(normal_test_data).numpy()
decoded_data = autoencoder.decoder(encoded_data).numpy()
plt.plot(normal_test_data[0], 'b')
plt.plot(decoded_data[0], 'r')
plt.fill_between(np.arange(140), decoded_data[0], normal_test_data[0], color='lightcoral')
plt.legend(labels=["Input", "Reconstruction", "Error"])
plt.show()
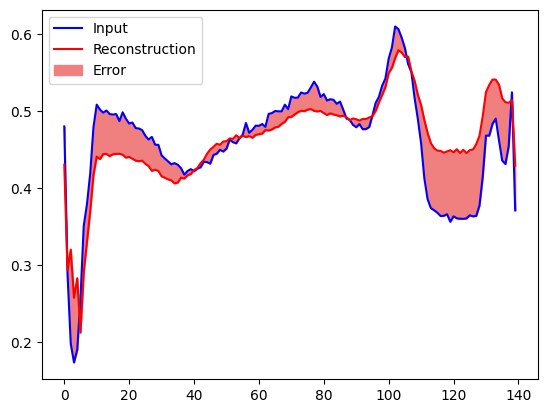
Create a similar plot, this time for an anomalous test example.
encoded_data = autoencoder.encoder(anomalous_test_data).numpy()
decoded_data = autoencoder.decoder(encoded_data).numpy()
plt.plot(anomalous_test_data[0], 'b')
plt.plot(decoded_data[0], 'r')
plt.fill_between(np.arange(140), decoded_data[0], anomalous_test_data[0], color='lightcoral')
plt.legend(labels=["Input", "Reconstruction", "Error"])
plt.show()
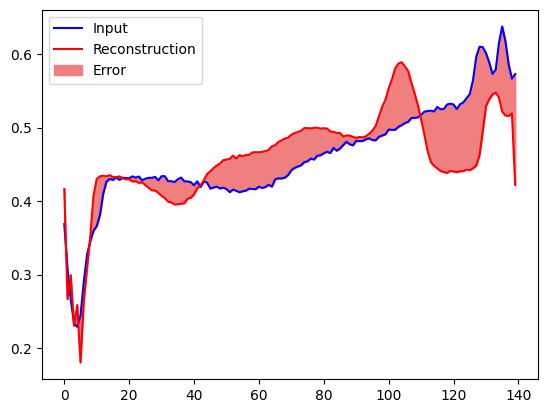
Detect anomalies
Detect anomalies by calculating whether the reconstruction loss is greater than a fixed threshold. In this tutorial, you will calculate the mean average error for normal examples from the training set, then classify future examples as anomalous if the reconstruction error is higher than one standard deviation from the training set.
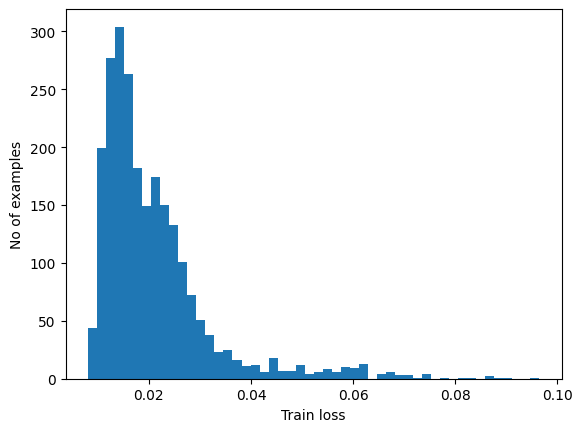
Plot the reconstruction error on normal ECGs from the training set
reconstructions = autoencoder.predict(normal_train_data)
train_loss = tf.keras.losses.mae(reconstructions, normal_train_data)
plt.hist(train_loss[None,:], bins=50)
plt.xlabel("Train loss")
plt.ylabel("No of examples")
plt.show()
74/74 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 5ms/step
Choose a threshold value that is one standard deviations above the mean.
threshold = np.mean(train_loss) + np.std(train_loss)
print("Threshold: ", threshold)
Threshold: 0.034314327
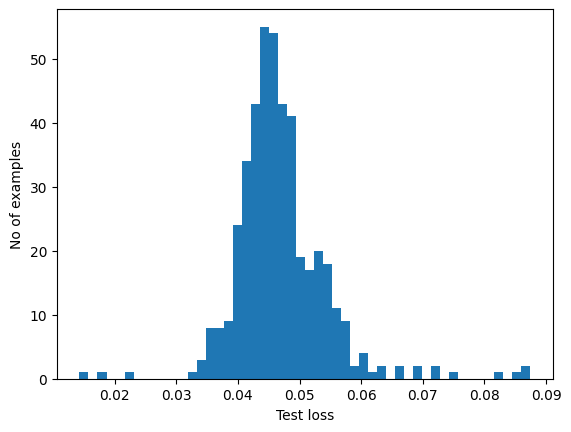
If you examine the reconstruction error for the anomalous examples in the test set, you'll notice most have greater reconstruction error than the threshold. By varing the threshold, you can adjust the precision and recall of your classifier.
reconstructions = autoencoder.predict(anomalous_test_data)
test_loss = tf.keras.losses.mae(reconstructions, anomalous_test_data)
plt.hist(test_loss[None, :], bins=50)
plt.xlabel("Test loss")
plt.ylabel("No of examples")
plt.show()
14/14 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 18ms/step
Classify an ECG as an anomaly if the reconstruction error is greater than the threshold.
def predict(model, data, threshold):
reconstructions = model(data)
loss = tf.keras.losses.mae(reconstructions, data)
return tf.math.less(loss, threshold)
def print_stats(predictions, labels):
print("Accuracy = {}".format(accuracy_score(labels, predictions)))
print("Precision = {}".format(precision_score(labels, predictions)))
print("Recall = {}".format(recall_score(labels, predictions)))
preds = predict(autoencoder, test_data, threshold)
print_stats(preds, test_labels)
Accuracy = 0.943 Precision = 0.9921722113502935 Recall = 0.9053571428571429
Next steps
To learn more about anomaly detection with autoencoders, check out this excellent interactive example built with TensorFlow.js by Victor Dibia. For a real-world use case, you can learn how Airbus Detects Anomalies in ISS Telemetry Data using TensorFlow. To learn more about the basics, consider reading this blog post by François Chollet. For more details, check out chapter 14 from Deep Learning by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville.
